Root Canal Explained
"Has your dentist told you that you need root canal treatment? If so, you're not alone. Millions of teeth are treated and saved each year with the root canal, or endodontic, treatment. This page explains root canal treatment in detail and how it can relieve your tooth pain and save your smile.
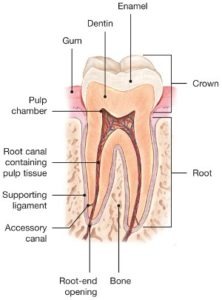 “Endo” is the Greek word for “inside” and “odont” is Greek for “tooth.” Endodontic treatment treats the inside of the tooth. Root canal treatment is one type of endodontic treatment.
“Endo” is the Greek word for “inside” and “odont” is Greek for “tooth.” Endodontic treatment treats the inside of the tooth. Root canal treatment is one type of endodontic treatment.
To understand endodontic treatment, it helps to know something about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is a soft tissue called the pulp. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves and connective tissue and creates the surrounding hard tissues of the tooth during development.
The pulp extends from the crown of the tooth to the tip of the roots where it connects to the tissues surrounding the root. The pulp is important during a tooth’s growth and development. However, once a tooth is fully mature it can survive without the pulp, because the tooth continues to be nourished by the tissues surrounding it.
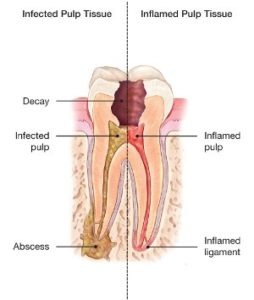
Signs to look for include pain, prolonged sensitivity to heat or cold, tenderness to touch and chewing, discoloration of the tooth, and swelling, drainage and tenderness in the lymph nodes as well as nearby bone and gum tissues. Sometimes, however, there are no symptoms.
 Endodontic treatment can often be performed in one or two visits and involves the following steps:
Endodontic treatment can often be performed in one or two visits and involves the following steps:- The endodontist examines and takes a radiograph of the tooth using x-rays, then administers local anesthetic. After the tooth is numb, the endodontist places a small protective sheet called a “dental dam” over the area to isolate the tooth and keep it clean and free of saliva during the procedure.
- The endodontist makes an opening in the crown of the tooth. Very small instruments are used to clean the pulp from the pulp
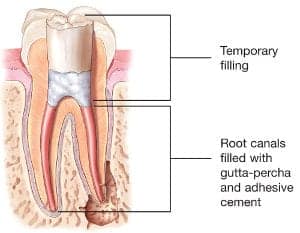
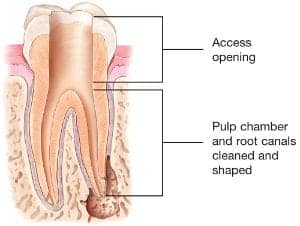 chamber and root canals and to shape the space for filling.
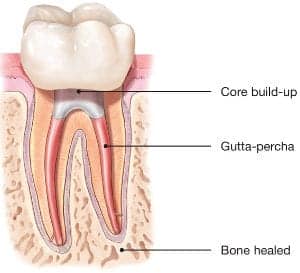
chamber and root canals and to shape the space for filling. - After space is cleaned and shaped, the endodontist fills the root canals with a biocompatible material, usually a rubber-like material called gutta-percha. The gutta-percha is placed with an adhesive cement to ensure complete sealing of the root canals. In most cases, a temporary filling is placed to close the opening. The temporary filling will be removed by your dentist before the tooth is restored.
- After the final visit with your endodontist, you must return to your dentist to have a crown or other restoration placed on the tooth to protect and restore it to full function.
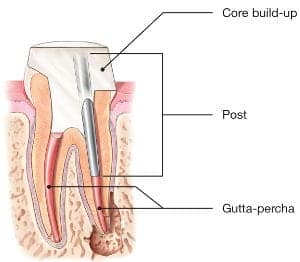
If the tooth lacks sufficient structure to hold the restoration in place, your dentist or endodontist may place a post inside the tooth. Ask your dentist or endodontist for more details about the specific restoration planned for your tooth.
All of this info and more can be found at https://www.aae.org/patients/root-canal-treatment/what-is-a-root-canal/root-canal-explained/".
Dr. Schemehorn is shown discussing the clinical overview of #root #canal #therapy with his lovely patient. Dr. Schemehorn has a wealth of clinical knowledge in the field of #endodontics, and has been serving the #Kokomo and #Peru communities for over 20 years! Give #LADD #Dental #Group a call today, and experience the difference of having a #comprehensive #dental #team working for you!
Comments
Post a Comment